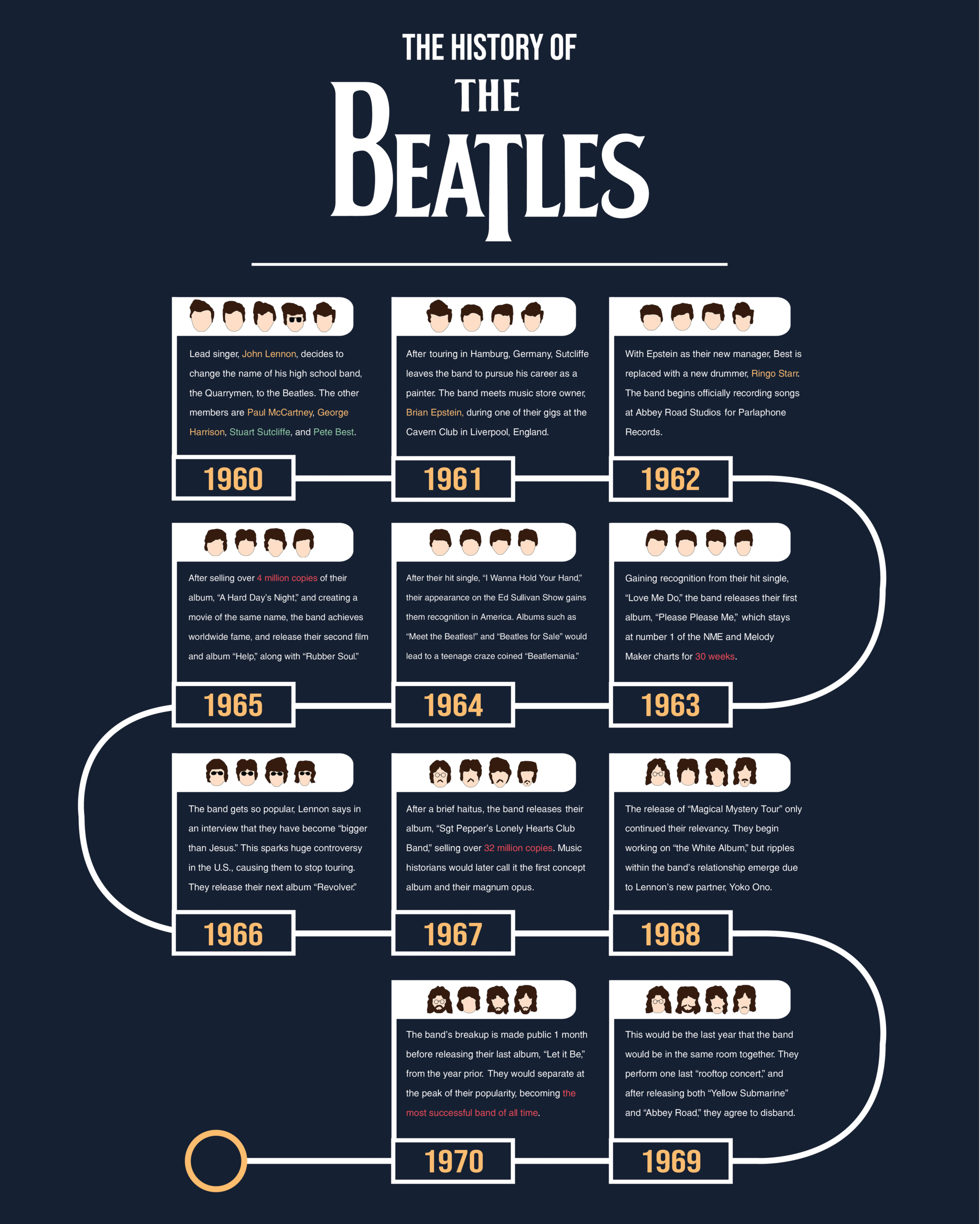
The Evolution of The Beatles: A Musical Journey Through the Years
The Beatles, often heralded as one of the most influential bands in the history of popular music, have left an indelible mark on the cultural landscape of the 20th century and beyond. From their humble beginnings in Liverpool to global superstardom, their evolution as artists reflects both personal growth and the shifting tides of musical innovation. This article explores the transformative journey of The Beatles through the decades, examining their early influences, groundbreaking innovations, and enduring legacy.
The Origins: Liverpool and Hamburg (Early 1960s)
The story of The Beatles begins in Liverpool in the late 1950s. Originally formed as The Quarrymen in 1957 by John Lennon, the band underwent several lineup changes before settling on the name “The Beatles” in 1960, inspired by Buddy Holly and The Crickets. The early lineup included Lennon, Paul McCartney, George Harrison, Stuart Sutcliffe, and later, Ringo Starr.
Their initial years were marked by relentless performances in clubs and venues across Liverpool and Hamburg, Germany. These formative experiences honed their musicianship and stage presence. Influenced by American rock and roll, rhythm and blues, and skiffle music, their early sound was energetic, raw, and rooted in the traditions of 1950s rock.
The British Invasion and Beatlemania (Mid-1960s)
By 1962, with the addition of Ringo Starr, The Beatles signed with EMI and released “Love Me Do,” which charted in the UK. Their second album, *With the Beatles* (1963), cemented their popularity. However, it was their third album, *A Hard Day’s Night* (1964), that marked their international breakthrough, coinciding with the start of Beatlemania—a cultural phenomenon that swept across Britain and America.
During these years, the band’s sound was characterized by catchy melodies, vocal harmonies, and innovative studio techniques. Albums like *Beatles for Sale* and *Help!* showcased their versatility, blending pop sensibilities with a growing sophistication. The Beatles’ influence extended beyond music; they became style icons and cultural ambassadors for the youth of the 1960s.
Artistic Maturity and Experimentation (Late 1960s)
By the mid-1960s, The Beatles began to push musical boundaries. The release of *Rubber Soul* (1965) and *Revolver* (1966) marked a shift toward more complex songwriting, lyrical depth, and experimentation with studio effects. Tracks like “Norwegian Wood” and “Tomorrow Never Knows” demonstrated their interest in folk, psychedelia, and avant-garde sounds.
The turning point came with the iconic album *Sgt. Pepper’s Lonely Hearts Club Band* (1967). Widely regarded as one of the greatest albums of all time, it exemplified artistic innovation, incorporating elaborate arrangements, multicultural influences, and concept-driven storytelling. The album challenged conventions of pop music and opened the door for future experimental works.
Following *Sgt. Pepper*, The Beatles continued to evolve with *Magical Mystery Tour* (1967), *The Beatles* (commonly known as the “White Album,” 1968), and *Abbey Road* (1969). These albums reflected a band exploring different genres—from the psychedelic sounds of “Lucy in the Sky with Diamonds” to the folk-rock of “Blackbird” and the experimental “Revolution 9.”
Personal and Artistic Divergence (Late 1960s – Early 1970s)
As the 1960s drew to a close, internal tensions surfaced. The members’ personal interests and creative visions began to diverge. John Lennon became increasingly interested in political activism and avant-garde art, while Paul McCartney focused on melody and craftsmanship. George Harrison explored Indian classical music, evident in songs like “Within You Without You.”
Despite their differences, they continued to produce influential music together, culminating in the release of Let It Be (1970). This album was marked by a more raw, live-in-the-studio sound, contrasting with the studio-polished Sgt. Pepper and Abbey Road.
The band officially disbanded in 1970, a decision influenced by personal conflicts, business disagreements, and creative differences. Nevertheless, their individual careers flourished, with each member pursuing solo projects that showcased their diverse talents.
Solo Years and Legacy
Post-breakup, The Beatles’ members embarked on varied paths. John Lennon released acclaimed solo work like *Imagine* (1971) and became a vocal advocate for peace. Paul McCartney’s band Wings produced multiple hits, and George Harrison achieved success with albums like *All Things Must Pass* (1970), featuring the hit “My Sweet Lord.” Ringo Starr also enjoyed a successful solo career, with hits like “Photograph.”
Throughout the 1970s and beyond, The Beatles’ influence persisted. Their innovative approach to songwriting, studio production, and album-oriented music set new standards in the industry. The reissue of their catalog, remastered editions, and anniversary celebrations continually introduced their work to new generations.
The Cultural Impact and Enduring Legacy
The Beatles’ evolution mirrors broader cultural shifts—changing attitudes toward youth, love, politics, and experimentation. Their willingness to embrace new sounds and ideas helped redefine what popular music could be.
Their influence extends beyond music to fashion, film, and social activism. The band’s pioneering use of studio techniques, such as multitracking and backward recording, laid the groundwork for future artists and producers. Their albums remain critically acclaimed, and songs like “Hey Jude,” “Let It Be,” and “Yesterday” continue to resonate worldwide.
In recent decades, The Beatles’ legacy has been preserved through documentaries, biographies, and tributes. The Beatles’ story is a testament to artistic growth, innovation, and the enduring power of music to unite and inspire.
Conclusion
From their roots in Liverpool to global stardom and beyond, The Beatles’ journey exemplifies the evolution of a band that constantly reinvented itself. Their early days of energetic cover performances evolved into groundbreaking studio experimentation and deeply personal songwriting. Their influence is woven into the fabric of modern music and culture, cementing their status as timeless icons.
The Beatles’ evolution is not just a story of musical development but also a reflection of a generation’s hopes, fears, and aspirations. As they continue to inspire artists and audiences worldwide, their legacy endures—an everlasting testament to creativity, innovation, and the transformative power of music.